Polygon Clipping Sutherland Hodgman Algorithm
A
polygon can be clipped by processing its boundary as a whole against
each window edge. This is achieved by processing all polygon vertices
against each clip rectangle boundary in turn. beginning with the
original set of polygon vertices, we could first clip the polygon
against the left rectangle boundary to produce a new sequence of
vertices. The new set of vertices could then be successively passed to a
right boundary clipper, a top boundary clipper and a bottom boundary
clipper. At each step a new set of polygon
vertices is generated and passed to the next window boundary clipper.
This is the fundamental idea used in the Sutherland - Hodgeman
algorithm.
Sutherland-Hodgeman Polygon Clipping Algorithm:-
- Read coordinates of all vertices of the Polygon.
- Read coordinates of the dipping window
- Consider the left edge of the window
- Compare the vertices of each edge of the polygon, individually with the clipping plane.
- Save the resulting intersections and vertices in the new list of
vertices according to four possible relationships between the edge and
the clipping boundary.
- Repeat the steps 4 and 5 for remaining edges or the clipping window.
Each time the resultant list of vertices is successively passed to
process the next edge of the clipping window.
- Stop.
Output Screenshots:
Code:
sketch.js:
function setup() {
createCanvas(600, 600);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
let window = new Window();
window.display();
let poly = new Polygon();
poly.refDisp();
strokeWeight(5)
stroke(0, 100, 100);
sutherClip(poly.vertices, poly.vertices.length, window.vertices,
window.vertices.length);
}
function xIntersect(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4) {
let nr = (x1 * y2 - y1 * x2) * (x3 - x4) - (x1 - x2) *
(x3 * y4 - y3 * x4);
let dr = (x1 - x2) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y2) * (x3 - x4);
return nr / dr;
}
function yIntersect(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4) {
let nr = (x1 * y2 - y1 * x2) * (y3 - y4) -
(y1 - y2) * (x3 * y4 - y3 * x4);
let dr = (x1 - x2) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y2) * (x3 - x4);
return nr / dr;
}
// clipping wrt one clip edge
function clip(polyVert, polySize, x1, y1, x2, y2) {
let newVert = [];
let newPolSize = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < polySize; i++) {
let k = (i + 1) % polySize;
let ix = polyVert[i][0];
let iy = polyVert[i][1];
let kx = polyVert[k][0];
let ky = polyVert[k][1];
// calculating position of first point wrt clipper line
let iPos = (x2 - x1) * (iy - y1) - (y2 - y1) * (ix - x1);
// calculating position of second point wrt clipper line
let kPos = (x2 - x1) * (ky - y1) - (y2 - y1) * (kx - x1);
// when both points are inside
if (iPos > 0 && kPos > 0) {
newVert[newPolSize] = [];
newVert[newPolSize][0] = kx;
newVert[newPolSize][1] = ky;
newPolSize++;
}
// when only first point is outside
else if (iPos <= 0 && kPos > 0) {
newVert[newPolSize] = [];
newVert[newPolSize][0] = xIntersect(x1, y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
newVert[newPolSize][1] = yIntersect(x1, y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
newPolSize++;
newVert[newPolSize] = [];
newVert[newPolSize][0] = kx;
newVert[newPolSize][1] = ky;
newPolSize++;
}
// when only second point is outside
else if (iPos > 0 && kPos <= 0) {
newVert[newPolSize] = [];
newVert[newPolSize][0] = xIntersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
newVert[newPolSize][1] = yIntersect(x1,
y1, x2, y2, ix, iy, kx, ky);
newPolSize++;
}
// when both points are outside
else {}
}
// copying new points into original array
polySize = newPolSize;
for (let i = 0; i < polySize; i++) {
polyVert[i] = [];
polyVert[i][0] = newVert[i][0];
polyVert[i][1] = newVert[i][1];
}
}
function sutherClip(polyVert, polySize, windowVert, windowSize) {
for (let i = 0; i < windowSize; i++) {
let k = (i + 1) % windowSize;
clip(polyVert, polySize, windowVert[i][0],
windowVert[i][1], windowVert[k][0],
windowVert[k][1]);
}
for (let i = 0; i < polySize; i++)
print(polyVert[i][0], polyVert[i][1]);
dispClip(polyVert);
}
function dispClip(finalPolyVert) {
for (let i = 0; i < finalPolyVert.length; i++) {
let k = (i + 1) % finalPolyVert.length;
line(finalPolyVert[i][0], finalPolyVert[i][1],
finalPolyVert[k][0], finalPolyVert[k][1]);
}
}
window.js:
class Window {
constructor() {
this.width = 300;
this.height = 250;
this.x = mouseX - (this.width / 2);
this.y = mouseY - (this.height / 2);
this.vertices = [[this.x, this.y], [this.x + this.width,
this.y], [this.x + this.width, this.y +
this.height], [this.x, this.y + this.height]];
}
display() {
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(1);
noFill();
rect(this.x, this.y, this.width, this.height);
}
}
polygon.js
class Polygon {
constructor() {
this.vertices = [[200, 250], [300, 350], [400, 300]];
}
refDisp() {
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(1);
for(let i = 0; i < this.vertices.length - 1; i++) {
line(this.vertices[i][0], this.vertices[i][1],
this.vertices[i + 1][0], this.vertices[i + 1][1]);
}
line(this.vertices[this.vertices.length - 1][0],
this.vertices[this.vertices.length - 1][1],
this.vertices[0][0], this.vertices[0][1]);
}
}














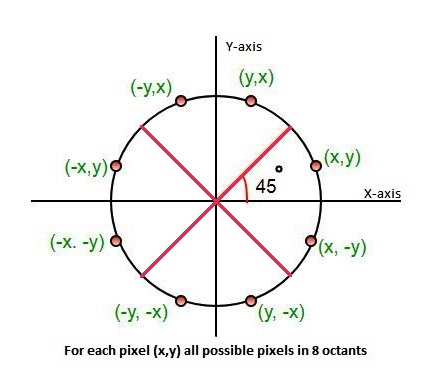 Point (x, y) is in the first octant and is on the circle.
Point (x, y) is in the first octant and is on the circle.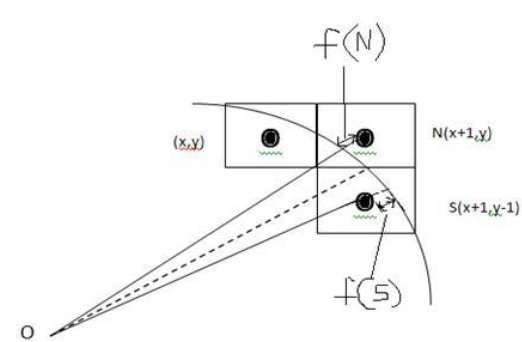 It is decided by using the decision parameter d as:
It is decided by using the decision parameter d as:



